The A3 Manual Transmission helps you review key topics like clutches, gearboxes, and axles. It’s a quick way to test your knowledge and prepare for the manual transmission certification exam.
Practice 3
Quiz-summary
0 of 50 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
Information
A3: Manual Transmission
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 50 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
1 pointsThe shifter on a light-duty truck’s manual transmission seems loose and has excessive play. Which of the following is MOST LIKELY to be the cause of this condition?
Correct
A worn shifter bushing is the most likely cause of a loose or overly sloppy shifter in a manual transmission. This small rubber or plastic component sits between the shifter linkage and the transmission, helping to maintain a tight, precise connection. Over time, the bushing can degrade or break, leading to excessive play in the shifter and making gear changes less accurate. In some cases, it may even cause the transmission to slip out of gear.
While issues like a bent shift rail or shift rod linkage could also result in a loose shifter, these problems are less common and usually present additional symptoms—such as difficulty engaging specific gears or grinding during shifts.
A worn detent ball and spring may cause hard shifting into certain gears but is unlikely to be the primary cause of a loose-feeling shifter.
Incorrect
A worn shifter bushing is the most likely cause of a loose or overly sloppy shifter in a manual transmission. This small rubber or plastic component sits between the shifter linkage and the transmission, helping to maintain a tight, precise connection. Over time, the bushing can degrade or break, leading to excessive play in the shifter and making gear changes less accurate. In some cases, it may even cause the transmission to slip out of gear.
While issues like a bent shift rail or shift rod linkage could also result in a loose shifter, these problems are less common and usually present additional symptoms—such as difficulty engaging specific gears or grinding during shifts.
A worn detent ball and spring may cause hard shifting into certain gears but is unlikely to be the primary cause of a loose-feeling shifter.
-
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
1 pointsTechnician A advises replacing the ring gear without changing the pinion gear as long as the specifications are met. Technician B recommends using a digital micrometer to measure the ring gear runout. Who could be CORRECT?
Correct
-
Technician A is incorrect in recommending the replacement of the ring gear without also replacing the pinion gear. The ring and pinion gears are matched as a set to ensure proper contact and wear patterns. Replacing only one of these components can result in poor gear mesh, increased noise, and premature failure.
-
Technician B is also incorrect in suggesting the use of a digital micrometer to measure ring gear runout. While a micrometer can accurately measure the diameter or thickness of a component, it is not suitable for checking runout. Runout refers to the amount of wobble or deviation as the ring gear rotates, which should be measured using a dial indicator for precise results.
-
Therefore, neither technician is correct. If ring gear damage is suspected, both the ring and pinion gears should be inspected and replaced as a matched set if necessary, and proper diagnostic tools like a dial indicator should be used to measure runout. A qualified technician should handle the inspection and repair to ensure reliability and performance.
Incorrect
-
Technician A is incorrect in recommending the replacement of the ring gear without also replacing the pinion gear. The ring and pinion gears are matched as a set to ensure proper contact and wear patterns. Replacing only one of these components can result in poor gear mesh, increased noise, and premature failure.
-
Technician B is also incorrect in suggesting the use of a digital micrometer to measure ring gear runout. While a micrometer can accurately measure the diameter or thickness of a component, it is not suitable for checking runout. Runout refers to the amount of wobble or deviation as the ring gear rotates, which should be measured using a dial indicator for precise results.
-
Therefore, neither technician is correct. If ring gear damage is suspected, both the ring and pinion gears should be inspected and replaced as a matched set if necessary, and proper diagnostic tools like a dial indicator should be used to measure runout. A qualified technician should handle the inspection and repair to ensure reliability and performance.
-
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
1 pointsWhen accelerating from a stop, a 4WD vehicle creates a popping sound. This sound is only heard in 4WD. Which of the following is the cause of this condition?Correct
A stretched transfer case chain is the most likely cause of a popping sound when accelerating from a stop in 4WD. This chain connects the transfer case output shaft to the front or rear driveshaft and transmits torque to the drivetrain. Over time, the chain can wear or stretch, leading to slack. When torque suddenly increases—such as during acceleration from a stop in 4WD—the loose chain can slip or jump teeth, creating a noticeable popping or banging noise.
A faulty relay or shift motor, which controls engagement of the 4WD system, is unlikely to produce this kind of noise. Similarly, low engine vacuum may affect systems like power brakes but would not typically result in a popping sound in 4WD operation.
Incorrect
A stretched transfer case chain is the most likely cause of a popping sound when accelerating from a stop in 4WD. This chain connects the transfer case output shaft to the front or rear driveshaft and transmits torque to the drivetrain. Over time, the chain can wear or stretch, leading to slack. When torque suddenly increases—such as during acceleration from a stop in 4WD—the loose chain can slip or jump teeth, creating a noticeable popping or banging noise.
A faulty relay or shift motor, which controls engagement of the 4WD system, is unlikely to produce this kind of noise. Similarly, low engine vacuum may affect systems like power brakes but would not typically result in a popping sound in 4WD operation.
-
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
1 pointsA transmission’s extension housing bushing is only worn on one side. According to Technician A, this form of wear is caused by binding universal joints. According to Technician B, this is due to excessive output shaft end-play. Who is CORRECT?Correct
A binding universal joint can cause one-sided wear on the extension housing bushing. The universal joint, which allows the driveshaft to flex and change angles smoothly, consists of two yokes connected by four trunnions with needle bearings. When the trunnions cannot rotate freely due to binding, it creates uneven movement and side-loading on the driveshaft, leading to localized wear on one side of the extension housing bushing.
While excessive output shaft end-play can also contribute to bushing wear, it typically results in more uniform wear rather than wear concentrated on one side. Therefore, a binding universal joint is the more likely cause of one-sided bushing damage.
Incorrect
A binding universal joint can cause one-sided wear on the extension housing bushing. The universal joint, which allows the driveshaft to flex and change angles smoothly, consists of two yokes connected by four trunnions with needle bearings. When the trunnions cannot rotate freely due to binding, it creates uneven movement and side-loading on the driveshaft, leading to localized wear on one side of the extension housing bushing.
While excessive output shaft end-play can also contribute to bushing wear, it typically results in more uniform wear rather than wear concentrated on one side. Therefore, a binding universal joint is the more likely cause of one-sided bushing damage.
-
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
1 pointsTwo technicians are discussing a vacuum-operated transfer case. Technician A states that this unit requires a vacuum between 10 “hg and 18 “hg. Technician B explains that the vacuum motor activates a mode fork to switch between 2WD and 4WD. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
A vacuum-operated transfer case requires a minimum of 15 inches of mercury (inHg) of vacuum to activate the motor. Transfer cases can be controlled through various methods, including manual, hydraulic, or electronic systems.
Technician B is correct in stating that the vacuum motor operates a mode fork to shift between 2WD and 4WD. When sufficient vacuum is applied, the vacuum motor moves the mode fork, engaging or disengaging the transfer case to switch the drivetrain mode accordingly.
Incorrect
A vacuum-operated transfer case requires a minimum of 15 inches of mercury (inHg) of vacuum to activate the motor. Transfer cases can be controlled through various methods, including manual, hydraulic, or electronic systems.
Technician B is correct in stating that the vacuum motor operates a mode fork to shift between 2WD and 4WD. When sufficient vacuum is applied, the vacuum motor moves the mode fork, engaging or disengaging the transfer case to switch the drivetrain mode accordingly.
-
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
1 pointsIn the picture below, what rear axle measurement is being performed?
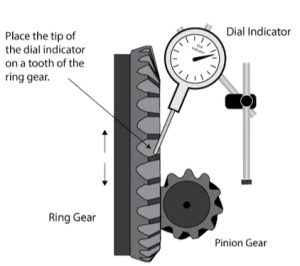 Correct
Correct
The photo shows a technician measuring backlash.
Backlash measurement is a crucial step when inspecting a rear axle, as it helps diagnose potential issues with the differential and gear alignment. Backlash refers to the slight clearance between the teeth of the ring gear and pinion gear when they are meshed. This gap ensures proper gear engagement and prevents excessive friction or noise during operation.
Incorrect
The photo shows a technician measuring backlash.
Backlash measurement is a crucial step when inspecting a rear axle, as it helps diagnose potential issues with the differential and gear alignment. Backlash refers to the slight clearance between the teeth of the ring gear and pinion gear when they are meshed. This gap ensures proper gear engagement and prevents excessive friction or noise during operation.
-
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
1 pointsWhile driving forward, a vehicle experiences vibration, which increases with vehicle speed. Which of the following is the LEAST LIKELY cause of this condition?
Correct
The limited slip clutch is the least likely cause of a vibration that increases with vehicle speed.
This clutch, located within the differential, helps distribute power evenly between the drive wheels. While a worn or faulty limited slip clutch can affect traction and handling, it typically does not produce speed-related vibrations.
In contrast, issues such as an unbalanced tire, worn U-joints, or excess undercoating on the driveshaft are common causes of vibration that worsens with speed. An unbalanced tire can cause the steering wheel to shake, while worn U-joints or driveshaft issues can create noticeable vibrations throughout the vehicle.
Incorrect
The limited slip clutch is the least likely cause of a vibration that increases with vehicle speed.
This clutch, located within the differential, helps distribute power evenly between the drive wheels. While a worn or faulty limited slip clutch can affect traction and handling, it typically does not produce speed-related vibrations.
In contrast, issues such as an unbalanced tire, worn U-joints, or excess undercoating on the driveshaft are common causes of vibration that worsens with speed. An unbalanced tire can cause the steering wheel to shake, while worn U-joints or driveshaft issues can create noticeable vibrations throughout the vehicle.
-
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
1 pointsWhen cornering, a front-wheel-drive vehicle creates a clicking sound. Technician A believes this is due to the axle’s (CV) constant velocity joint. Technician B believes it is the torsional damper on the axle shaft. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
A clicking sound while cornering is a common sign of a worn or damaged constant velocity (CV) joint. CV joints allow the axle shaft to transfer power from the transmission to the wheels while accommodating suspension movement and steering angles. When a CV joint becomes worn or damaged, it can produce a clicking or popping noise during turns, especially under acceleration.
The torsional damper, on the other hand, is designed to reduce vibrations in the axle shaft and is not typically linked to clicking noises when turning.
Incorrect
A clicking sound while cornering is a common sign of a worn or damaged constant velocity (CV) joint. CV joints allow the axle shaft to transfer power from the transmission to the wheels while accommodating suspension movement and steering angles. When a CV joint becomes worn or damaged, it can produce a clicking or popping noise during turns, especially under acceleration.
The torsional damper, on the other hand, is designed to reduce vibrations in the axle shaft and is not typically linked to clicking noises when turning.
-
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
1 pointsTechnician A says U-joints must be in phase to prevent vibration. On re-assembling a drive shaft, the u-joints don’t need to be in alignment for proper operation if they are greased with the proper lubricant, says Technician B. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Technician A is correct.
U-joints must be properly phased to prevent vibration. If they are out of phase, the driveshaft can vibrate excessively, potentially causing damage to the driveshaft, U-joints, and surrounding components.Technician B is incorrect. While proper lubrication is important for the durability and smooth operation of U-joints, it does not address alignment issues. Greasing the joints will not eliminate vibrations caused by incorrect U-joint phasing. Proper alignment is essential for correct function.
Incorrect
Technician A is correct.
U-joints must be properly phased to prevent vibration. If they are out of phase, the driveshaft can vibrate excessively, potentially causing damage to the driveshaft, U-joints, and surrounding components.Technician B is incorrect. While proper lubrication is important for the durability and smooth operation of U-joints, it does not address alignment issues. Greasing the joints will not eliminate vibrations caused by incorrect U-joint phasing. Proper alignment is essential for correct function.
-
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
1 pointsA clutch pressure plate is being discussed by two technicians. If the pressure plate is warped, Technician A recommends replacing it. According to Technician B, the pressure plate is simply disassembled and fixed or resurfaced. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
If a clutch pressure plate is warped, resurfacing or machining will not correct the issue. Warping causes the plate to become uneven, leading to clutch engagement problems, slippage, and poor performance. In such cases, the only effective solution is to replace the pressure plate.
Although a pressure plate can sometimes be disassembled and resurfaced for minor surface imperfections, this process does not resolve warping. A warped pressure plate must be replaced to ensure proper clutch operation.
Incorrect
If a clutch pressure plate is warped, resurfacing or machining will not correct the issue. Warping causes the plate to become uneven, leading to clutch engagement problems, slippage, and poor performance. In such cases, the only effective solution is to replace the pressure plate.
Although a pressure plate can sometimes be disassembled and resurfaced for minor surface imperfections, this process does not resolve warping. A warped pressure plate must be replaced to ensure proper clutch operation.
-
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
1 pointsWhich of the following is the MOST likely reason for a transaxle jumping out of gear under load?
Correct
The shift linkage is a system of rods and cables that connects the gear shifter to the transmission, enabling smooth and precise gear changes. If the linkage is loose, worn, or improperly adjusted, it can lead to the transmission slipping out of gear.
Incorrect
The shift linkage is a system of rods and cables that connects the gear shifter to the transmission, enabling smooth and precise gear changes. If the linkage is loose, worn, or improperly adjusted, it can lead to the transmission slipping out of gear.
-
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
1 pointsA 6-speed manual transmission with a hydraulic clutch shifts slowly and creeps into gear. According to Technician A, there could be air in the hydraulic fluid. According to Technician B, this issue can be caused by excessive clutch pedal free travel. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Air in the hydraulic fluid can prevent the clutch from fully disengaging from the flywheel, leading to difficulty shifting and the vehicle creeping into gear. This happens because the air compresses within the hydraulic system, reducing the pressure needed to operate the clutch properly.
Similarly, excessive clutch pedal free travel can also cause incomplete disengagement of the clutch. When the clutch doesn’t fully release, it can result in slow or difficult shifting and may cause gear grinding when attempting to shift.
Incorrect
Air in the hydraulic fluid can prevent the clutch from fully disengaging from the flywheel, leading to difficulty shifting and the vehicle creeping into gear. This happens because the air compresses within the hydraulic system, reducing the pressure needed to operate the clutch properly.
Similarly, excessive clutch pedal free travel can also cause incomplete disengagement of the clutch. When the clutch doesn’t fully release, it can result in slow or difficult shifting and may cause gear grinding when attempting to shift.
-
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
1 pointsAccording to Technician A, the tool seen in this picture is utilized to center and align the transmission’s clutch disc. Technician B says the tool is similar to the transmission’s input shaft. Who is CORRECT?
 Correct
Correct
Both technicians are correct. The alignment tool is used to center and align the clutch friction disc during installation. The clutch pilot bearing—whether it’s a ball bearing, roller bearing, or brass bushing—supports and guides the transmission’s input shaft into the crankshaft flange. The alignment tool is designed to mimic the shape and size of the transmission’s input shaft to ensure proper positioning of the disc and pilot bearing.
Incorrect
Both technicians are correct. The alignment tool is used to center and align the clutch friction disc during installation. The clutch pilot bearing—whether it’s a ball bearing, roller bearing, or brass bushing—supports and guides the transmission’s input shaft into the crankshaft flange. The alignment tool is designed to mimic the shape and size of the transmission’s input shaft to ensure proper positioning of the disc and pilot bearing.
-
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
1 pointsWhen the clutch pedal is depressed, a chirping sound is heard from the inside of the bellhousing. Which of the following is MOST LIKELY to be the source of this noise?
Correct
The release bearing is the most likely cause of a chirping sound coming from the bellhousing when the clutch pedal is pressed.
This bearing, located inside the bellhousing, is responsible for disengaging the clutch when the pedal is depressed. Over time, it can wear out or become damaged, leading to a chirping or squealing noise during operation.
Although other components like a worn synchronizer assembly, clutch disc, or input shaft bearing can cause transmission noise, they are not typically located within the bellhousing and are less likely to produce a chirping sound specifically when the clutch pedal is engaged.
Incorrect
The release bearing is the most likely cause of a chirping sound coming from the bellhousing when the clutch pedal is pressed.
This bearing, located inside the bellhousing, is responsible for disengaging the clutch when the pedal is depressed. Over time, it can wear out or become damaged, leading to a chirping or squealing noise during operation.
Although other components like a worn synchronizer assembly, clutch disc, or input shaft bearing can cause transmission noise, they are not typically located within the bellhousing and are less likely to produce a chirping sound specifically when the clutch pedal is engaged.
-
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
1 pointsThere is a whining sound that rises with vehicle speed after a rear differential overhaul. Which of the following could be the cause?
Correct
After a rear differential overhaul, setting the side bearing preload correctly is essential. This preload refers to the force applied to the bearings that support the differential assembly. If it’s not properly adjusted, it can lead to a whining noise as the differential rotates.
While the side gears and spider gears are internal parts of the differential, they are not typically adjusted or replaced during a standard overhaul. Although worn or damaged gears could cause noise, this is less common than issues related to incorrect bearing preload.
Therefore, if a whining sound is heard after reassembly, the side bearing preload should be checked first to ensure it has been set to the proper specification.
Incorrect
After a rear differential overhaul, setting the side bearing preload correctly is essential. This preload refers to the force applied to the bearings that support the differential assembly. If it’s not properly adjusted, it can lead to a whining noise as the differential rotates.
While the side gears and spider gears are internal parts of the differential, they are not typically adjusted or replaced during a standard overhaul. Although worn or damaged gears could cause noise, this is less common than issues related to incorrect bearing preload.
Therefore, if a whining sound is heard after reassembly, the side bearing preload should be checked first to ensure it has been set to the proper specification.
-
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
1 pointsShift forks
___________.Correct
Shift forks are usually securely mounted to the shift rail and are designed to fit precisely into the synchronizer sleeve. Their primary function is to move the synchronizer sleeve back and forth along the transmission shaft, enabling gear engagement and disengagement. For smooth and accurate gear changes, the shift fork must be firmly attached to the shift rail. Additionally, the fork’s shape and dimensions must closely match the synchronizer sleeve to ensure proper alignment and reliable gear engagement.
Incorrect
Shift forks are usually securely mounted to the shift rail and are designed to fit precisely into the synchronizer sleeve. Their primary function is to move the synchronizer sleeve back and forth along the transmission shaft, enabling gear engagement and disengagement. For smooth and accurate gear changes, the shift fork must be firmly attached to the shift rail. Additionally, the fork’s shape and dimensions must closely match the synchronizer sleeve to ensure proper alignment and reliable gear engagement.
-
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
1 pointsDuring acceleration, a manual transmission shifts out of gear. According to Technician A, this situation is caused by a loose shift linkage. According to Technician B, worn motor mounts cause a transmission to slip out of gear. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
A loose shift linkage can cause a manual transmission to pop out of gear during acceleration. When the linkage isn’t secure, it can allow unwanted movement of the shifter, leading to improper gear engagement or disengagement under load.
Similarly, worn motor mounts can also cause the transmission to shift out of gear. Excessive engine movement from damaged mounts can place strain on the transmission and shift linkage, disrupting gear alignment and causing the transmission to disengage during acceleration.
Incorrect
A loose shift linkage can cause a manual transmission to pop out of gear during acceleration. When the linkage isn’t secure, it can allow unwanted movement of the shifter, leading to improper gear engagement or disengagement under load.
Similarly, worn motor mounts can also cause the transmission to shift out of gear. Excessive engine movement from damaged mounts can place strain on the transmission and shift linkage, disrupting gear alignment and causing the transmission to disengage during acceleration.
-
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
1 pointsTo check for flywheel runout, Technician A recommends using a dial indicator. However, Technician B recommend using this tool to check for crankshaft endplay. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Technician A is correct in recommending the use of a dial indicator to measure flywheel runout. Flywheel runout refers to any side-to-side wobble or uneven rotation of the flywheel, which can lead to vibrations and clutch issues. A dial indicator is the standard tool for checking runout and determining whether the flywheel should be resurfaced or replaced.
Technician B is also correct in suggesting a dial indicator to measure crankshaft endplay. Endplay is the amount of axial (back-and-forth) movement of the crankshaft within the engine block. It is typically measured with a dial indicator mounted on a magnetic base or, in some cases, with a feeler gauge to ensure the movement falls within the manufacturer’s specified tolerance.
Incorrect
Technician A is correct in recommending the use of a dial indicator to measure flywheel runout. Flywheel runout refers to any side-to-side wobble or uneven rotation of the flywheel, which can lead to vibrations and clutch issues. A dial indicator is the standard tool for checking runout and determining whether the flywheel should be resurfaced or replaced.
Technician B is also correct in suggesting a dial indicator to measure crankshaft endplay. Endplay is the amount of axial (back-and-forth) movement of the crankshaft within the engine block. It is typically measured with a dial indicator mounted on a magnetic base or, in some cases, with a feeler gauge to ensure the movement falls within the manufacturer’s specified tolerance.
-
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
1 pointsA client tows in a vehicle with a faulty U-joint. Technician A believes it can be repaired and approved to keep on using in the future. Technician B states this U-joint must be replaced before the client could drive the vehicle again. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
U-joints are a vital component of the vehicle’s drivetrain and should be replaced once they have failed. Reinstalling a repaired or used U-joint can leave it vulnerable to failure under load, potentially causing further damage to the drivetrain. Therefore, Technician B is correct in recommending the replacement of the faulty U-joint as the proper and reliable solution.
Incorrect
U-joints are a vital component of the vehicle’s drivetrain and should be replaced once they have failed. Reinstalling a repaired or used U-joint can leave it vulnerable to failure under load, potentially causing further damage to the drivetrain. Therefore, Technician B is correct in recommending the replacement of the faulty U-joint as the proper and reliable solution.
-
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
1 pointsWhich technician’s theory about the cause of a loud noise in a transfer case when the vehicle is moving, but not in neutral, is plausible? Technician A, who thinks the noise could be caused by a worn and loose drive chain hitting the inside of the case, or Technician B, who thinks a faulty transfer case bearing could be the cause?
Correct
Technician A’s suggestion that a worn and loose drive chain could be the source of the noise is plausible. A stretched chain may slap against the inside of the transfer case, producing a noticeable sound. However, other potential causes should also be considered.
Technician B is also correct in stating that a faulty transfer case bearing could be responsible. A worn or damaged bearing can generate a loud noise as the transfer case operates, especially under load. Both possibilities warrant inspection during diagnosis.
Incorrect
Technician A’s suggestion that a worn and loose drive chain could be the source of the noise is plausible. A stretched chain may slap against the inside of the transfer case, producing a noticeable sound. However, other potential causes should also be considered.
Technician B is also correct in stating that a faulty transfer case bearing could be responsible. A worn or damaged bearing can generate a loud noise as the transfer case operates, especially under load. Both possibilities warrant inspection during diagnosis.
-
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
1 pointsCase bearing preload is accurate in the shim-type differential, but the backlash seems a bit higher. How could you adjust this?
Correct
If the bearing preload is correct in a shim-type differential but the backlash is excessive, the proper adjustment is to remove shims from the right side and add an equal amount to the left side. This shifts the differential assembly to the left, reducing backlash and improving the engagement between the ring and pinion gears.
Incorrect
If the bearing preload is correct in a shim-type differential but the backlash is excessive, the proper adjustment is to remove shims from the right side and add an equal amount to the left side. This shifts the differential assembly to the left, reducing backlash and improving the engagement between the ring and pinion gears.
-
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
1 pointsA five-speed manual transmission is difficult to shift, and gold-colored shavings can be observed in the transmission fluid towards the end of the draining cycle. Which of the following is the source of this condition?
Correct
The most likely cause of a difficult-to-shift five-speed manual transmission accompanied by gold-colored shavings in the transmission fluid is worn synchronizer blocking rings.
These gold-colored shavings indicate metal wear, typically from softer metals like brass or bronze—materials commonly used in synchronizer rings. As these rings wear down from repeated friction and pressure during gear changes, they lose their ability to properly match gear speeds, resulting in hard shifting and metal debris in the fluid.
While chipped gear teeth can also cause shifting issues and metal contamination, they usually produce larger, silver-colored fragments. The presence of fine, gold-colored shavings points more directly to synchronizer wear.
Loose shift rails may contribute to shifting problems but are unlikely to produce gold-colored debris. Likewise, casting slag is a manufacturing byproduct and is not typically associated with shifting difficulty or this type of metal wear.
Incorrect
The most likely cause of a difficult-to-shift five-speed manual transmission accompanied by gold-colored shavings in the transmission fluid is worn synchronizer blocking rings.
These gold-colored shavings indicate metal wear, typically from softer metals like brass or bronze—materials commonly used in synchronizer rings. As these rings wear down from repeated friction and pressure during gear changes, they lose their ability to properly match gear speeds, resulting in hard shifting and metal debris in the fluid.
While chipped gear teeth can also cause shifting issues and metal contamination, they usually produce larger, silver-colored fragments. The presence of fine, gold-colored shavings points more directly to synchronizer wear.
Loose shift rails may contribute to shifting problems but are unlikely to produce gold-colored debris. Likewise, casting slag is a manufacturing byproduct and is not typically associated with shifting difficulty or this type of metal wear.
-
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
1 pointsTechnician A says an incorrect rear “U” joint operating angle can cause a vibration at high speed. Technician B thinks a squeaking noise in reverse is the result of a worn cross shaft bearing surface. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Technician A is referring to the driveline angle—the angle between the transmission output shaft and the rear differential input shaft. An incorrect driveline angle can lead to vibrations at higher speeds. However, other factors like unbalanced tires or worn suspension components can also cause similar vibration issues.
Technician B points to a specific symptom: a squeaking noise when the vehicle is in reverse. This can indeed be caused by a worn cross shaft bearing surface in the rear U-joint. Still, other possible sources of squeaking noises include worn brake pads or a damaged wheel bearing.
Incorrect
Technician A is referring to the driveline angle—the angle between the transmission output shaft and the rear differential input shaft. An incorrect driveline angle can lead to vibrations at higher speeds. However, other factors like unbalanced tires or worn suspension components can also cause similar vibration issues.
Technician B points to a specific symptom: a squeaking noise when the vehicle is in reverse. This can indeed be caused by a worn cross shaft bearing surface in the rear U-joint. Still, other possible sources of squeaking noises include worn brake pads or a damaged wheel bearing.
-
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
1 pointsAll of the statements are correct when installing and removing axle shafts, EXCEPT
_________.Correct
The statement “the shaft closest to the seal area needs to be inspected and then repaired with sandpaper as needed” is incorrect. Sandpaper should not be used on the shaft near the seal, as it can leave scratches that may compromise the sealing surface and lead to leaks. The proper procedure is to clean the shaft with a suitable solvent and apply a light coat of grease to protect the seal and ensure proper sealing.
The other statements are accurate:
-
Axle shaft seals should be replaced, not reused, as they can be easily damaged during removal or installation.
-
A slide hammer is often required when removing certain types of axles, especially those that are stuck or tightly fitted.
-
An axle shaft should not be stored or held upright, as doing so can cause the grease in the seal area to drain out, potentially leading to seal failure.
Incorrect
The statement “the shaft closest to the seal area needs to be inspected and then repaired with sandpaper as needed” is incorrect. Sandpaper should not be used on the shaft near the seal, as it can leave scratches that may compromise the sealing surface and lead to leaks. The proper procedure is to clean the shaft with a suitable solvent and apply a light coat of grease to protect the seal and ensure proper sealing.
The other statements are accurate:
-
Axle shaft seals should be replaced, not reused, as they can be easily damaged during removal or installation.
-
A slide hammer is often required when removing certain types of axles, especially those that are stuck or tightly fitted.
-
An axle shaft should not be stored or held upright, as doing so can cause the grease in the seal area to drain out, potentially leading to seal failure.
-
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
1 pointsBefore removing the flywheel, Technician A recommends making index marks on both the flywheel and the crankshaft. According to Technician B, removing too much surface from the flywheel can cause damage to the clutch release bearing. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
When removing the flywheel, it’s important to make index marks on both the flywheel and the crankshaft. These marks serve as reference points to ensure the flywheel is reinstalled in the same orientation. Proper alignment is critical for engine balance and smooth operation.
Technician B’s comment about removing too much material from the flywheel affecting the clutch release bearing is not relevant to the context of marking the flywheel. While excessive resurfacing can cause clutch-related issues, such as poor engagement or added stress on the release bearing, it does not pertain to the importance of indexing the flywheel prior to removal.
Incorrect
When removing the flywheel, it’s important to make index marks on both the flywheel and the crankshaft. These marks serve as reference points to ensure the flywheel is reinstalled in the same orientation. Proper alignment is critical for engine balance and smooth operation.
Technician B’s comment about removing too much material from the flywheel affecting the clutch release bearing is not relevant to the context of marking the flywheel. While excessive resurfacing can cause clutch-related issues, such as poor engagement or added stress on the release bearing, it does not pertain to the importance of indexing the flywheel prior to removal.
-
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
1 pointsA growling sound is made by a manual transmission, which becomes louder in second gear. According to Technician A, the second gear has a chipped tooth. According to Technician B, the blocking rings on the synchronizer are rounded. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Chipped or rounded gear teeth can produce a growling or grinding noise, especially when the affected gear is engaged. While the noise may be present in all gears, it tends to be more noticeable in the selected gear due to the increased load it carries. Gear teeth are engineered to mesh smoothly, and any damage—such as chipping or rounding—disrupts this contact, leading to irregular engagement and resulting in noise during operation.
Incorrect
Chipped or rounded gear teeth can produce a growling or grinding noise, especially when the affected gear is engaged. While the noise may be present in all gears, it tends to be more noticeable in the selected gear due to the increased load it carries. Gear teeth are engineered to mesh smoothly, and any damage—such as chipping or rounding—disrupts this contact, leading to irregular engagement and resulting in noise during operation.
-
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
1 pointsTechnician A thinks that the drive shafts on a FWD (front wheel drive) vehicle are usually removed with a pry bar or special puller. Technician B believes that the axle nuts on a FWD vehicle are not reusable. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Technician A is correct: On front-wheel drive (FWD) vehicles, removing the drive shafts—commonly referred to as CV (constant velocity) axles—often requires a pry bar or a special puller. These axles can become stuck due to corrosion or wear, and specialized tools are typically needed to safely disengage them from the hub or transmission without causing damage.
Technician B is also correct: Axle nuts on FWD vehicles are generally considered non-reusable. These nuts are torque-to-yield fasteners, meaning they are stretched during installation to apply the correct preload on the wheel bearings. Reusing them can compromise that preload, increasing the risk of bearing failure. For this reason, manufacturers recommend replacing the axle nuts any time the axle assembly is serviced.
Incorrect
Technician A is correct: On front-wheel drive (FWD) vehicles, removing the drive shafts—commonly referred to as CV (constant velocity) axles—often requires a pry bar or a special puller. These axles can become stuck due to corrosion or wear, and specialized tools are typically needed to safely disengage them from the hub or transmission without causing damage.
Technician B is also correct: Axle nuts on FWD vehicles are generally considered non-reusable. These nuts are torque-to-yield fasteners, meaning they are stretched during installation to apply the correct preload on the wheel bearings. Reusing them can compromise that preload, increasing the risk of bearing failure. For this reason, manufacturers recommend replacing the axle nuts any time the axle assembly is serviced.
-
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
1 pointsThe part pictured below contains
_________. Correct
Correct
All of the above statements are correct. The image shows a hub and bearing assembly with an ABS tone ring attached. The hub uses a sealed bearing and plays a critical role in supporting the vehicle’s weight during acceleration, braking, and cornering.
In ABS-equipped systems, wheel speed is monitored by sensors that detect the passing teeth of the tone (or reluctor) ring. Many modern hub assemblies integrate the wheel speed sensor or tone ring directly into their design for more accurate ABS function and improved durability.
Incorrect
All of the above statements are correct. The image shows a hub and bearing assembly with an ABS tone ring attached. The hub uses a sealed bearing and plays a critical role in supporting the vehicle’s weight during acceleration, braking, and cornering.
In ABS-equipped systems, wheel speed is monitored by sensors that detect the passing teeth of the tone (or reluctor) ring. Many modern hub assemblies integrate the wheel speed sensor or tone ring directly into their design for more accurate ABS function and improved durability.
-
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
1 pointsWhen the engine is running and the clutch is fully engaged, a manual transmission generates a grinding sound at the front of the transmission. Which of the following is the cause of this noise?
Correct
The input shaft bearing supports the input shaft, which links the clutch to the transmission. When this bearing becomes worn or damaged, it can cause the input shaft to wobble, often resulting in a grinding noise, particularly at the front of the transmission.
While other components—such as the clutch release bearing, output shaft bearing, or pilot bearing—can also create noise in a manual transmission, they are less likely to produce a grinding sound in this specific location. To ensure accurate diagnosis and proper repair, it’s recommended to have a qualified mechanic inspect the transmission and identify the exact source of the noise.
Incorrect
The input shaft bearing supports the input shaft, which links the clutch to the transmission. When this bearing becomes worn or damaged, it can cause the input shaft to wobble, often resulting in a grinding noise, particularly at the front of the transmission.
While other components—such as the clutch release bearing, output shaft bearing, or pilot bearing—can also create noise in a manual transmission, they are less likely to produce a grinding sound in this specific location. To ensure accurate diagnosis and proper repair, it’s recommended to have a qualified mechanic inspect the transmission and identify the exact source of the noise.
-
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
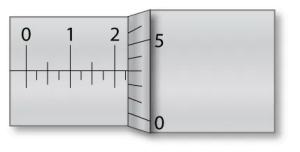
1 pointsThe reading on the outside micrometer indicates
_________. Correct
Correct
The micrometer shown above is an inch-based model, with graduations in thousandths of an inch. The measurement displayed is 0.228″.
Incorrect
The micrometer shown above is an inch-based model, with graduations in thousandths of an inch. The measurement displayed is 0.228″.
-
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
1 pointsWhat is the MOST PROBABLE cause for a broken center adapter plate, rear extension housing mating surface, or transmission case?
Correct
A damaged transmission case can result in an oil leak and may also indicate potential damage to the rear extension housing mating surface or center adapter plate. Cracks or other damage to the transmission case can allow fluid to escape, leading to low transmission fluid levels and possible harm to internal components.
Moreover, damage to the case can place extra stress on the rear extension housing or center adapter plate, increasing the risk of failure in those areas. Other unrelated issues are unlikely to occur as a direct result of these specific component failures.
Incorrect
A damaged transmission case can result in an oil leak and may also indicate potential damage to the rear extension housing mating surface or center adapter plate. Cracks or other damage to the transmission case can allow fluid to escape, leading to low transmission fluid levels and possible harm to internal components.
Moreover, damage to the case can place extra stress on the rear extension housing or center adapter plate, increasing the risk of failure in those areas. Other unrelated issues are unlikely to occur as a direct result of these specific component failures.
-
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
1 pointsOnly when cornering is a growling sound spotted from the rear of a rear-wheel-drive vehicle. Technician A says incorrect drive pinion bearing preload could be the reason. Technician B thinks faulty rear axle bearings could be the reason. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
A growling noise from the rear of a rear-wheel-drive vehicle during cornering is most commonly a sign of a worn or failing rear axle bearing. These bearings support the vehicle’s weight and enable smooth wheel rotation. When they become worn or damaged, they can produce a growling or rumbling sound, especially noticeable while turning due to the added lateral load.
Although incorrect drive pinion bearing preload can cause noise in the differential, it is less likely to produce a growling sound specifically during cornering.
Incorrect
A growling noise from the rear of a rear-wheel-drive vehicle during cornering is most commonly a sign of a worn or failing rear axle bearing. These bearings support the vehicle’s weight and enable smooth wheel rotation. When they become worn or damaged, they can produce a growling or rumbling sound, especially noticeable while turning due to the added lateral load.
Although incorrect drive pinion bearing preload can cause noise in the differential, it is less likely to produce a growling sound specifically during cornering.
-
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
1 pointsThe ring gear to pinion backlash is too low. This results in the ring gear tooth pattern to connect in what way to the following spots?
Correct
The term “toe contact” describes a condition where the contact between the ring gear and pinion teeth is concentrated near the toe, or inner edge, of the gear teeth. This typically results from insufficient backlash—the small amount of clearance between the ring gear and pinion.
When toe contact occurs, the contact pattern appears primarily at the inner edges of the teeth on both the drive (convex) and coast (concave) sides. This uneven contact is caused by improper alignment due to the reduced backlash, preventing the load from being evenly distributed across the entire tooth surface.
Incorrect
The term “toe contact” describes a condition where the contact between the ring gear and pinion teeth is concentrated near the toe, or inner edge, of the gear teeth. This typically results from insufficient backlash—the small amount of clearance between the ring gear and pinion.
When toe contact occurs, the contact pattern appears primarily at the inner edges of the teeth on both the drive (convex) and coast (concave) sides. This uneven contact is caused by improper alignment due to the reduced backlash, preventing the load from being evenly distributed across the entire tooth surface.
-
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
1 pointsWhen turning left, a front-wheel-drive passenger vehicle creates a growling sound that becomes louder. Which of the following is the cause of this noise?
Correct
Wheel bearings enable the wheels to rotate smoothly while supporting the vehicle’s weight. When a wheel bearing becomes worn or damaged, it can create a growling or grinding noise, particularly noticeable when the vehicle turns. In this scenario, turning left shifts the vehicle’s weight to the right front wheel, putting additional load on the faulty bearing and making the noise more pronounced.
Incorrect
Wheel bearings enable the wheels to rotate smoothly while supporting the vehicle’s weight. When a wheel bearing becomes worn or damaged, it can create a growling or grinding noise, particularly noticeable when the vehicle turns. In this scenario, turning left shifts the vehicle’s weight to the right front wheel, putting additional load on the faulty bearing and making the noise more pronounced.
-
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
1 pointsAfter shifting from 2WH to 4WH, the indicator light continues to flash. The shift is not completed, and the vehicle remains in 2WH. This issue could be caused by a faulty shift motor, according to Technician A. According to Technician B, this situation is caused by a bent actuator shift fork. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Technician A is correct in stating that a faulty shift motor could cause this issue. The shift motor controls the engagement of the transfer case, moving it into the selected drive mode. If the motor is malfunctioning, it may fail to position the transfer case correctly, leading to a failed shift and a flashing indicator light.
Technician B is also correct that a bent actuator shift fork could be the cause. The shift fork moves the shift collar to engage the desired gear. If it is bent or damaged, it may prevent proper gear engagement, resulting in a failed shift and a flashing indicator light.
Therefore, both technicians present valid potential causes of the problem.
Incorrect
Technician A is correct in stating that a faulty shift motor could cause this issue. The shift motor controls the engagement of the transfer case, moving it into the selected drive mode. If the motor is malfunctioning, it may fail to position the transfer case correctly, leading to a failed shift and a flashing indicator light.
Technician B is also correct that a bent actuator shift fork could be the cause. The shift fork moves the shift collar to engage the desired gear. If it is bent or damaged, it may prevent proper gear engagement, resulting in a failed shift and a flashing indicator light.
Therefore, both technicians present valid potential causes of the problem.
-
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
1 pointsOnly when the clutch pedal is entirely depressed to the floor could a squeal be heard from the clutch housing. According to Technician A, this could be due to worn countershaft bearings. Technician B believes the squeal is caused by a faulty pilot bearing. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
A faulty pilot bearing is the most likely source of a squealing noise coming from the clutch housing when the clutch pedal is pressed. This small bearing, located between the engine crankshaft and the transmission input shaft, allows the input shaft to rotate smoothly when the engine is running but the clutch is disengaged. If the pilot bearing is worn or damaged, it
Incorrect
A faulty pilot bearing is the most likely source of a squealing noise coming from the clutch housing when the clutch pedal is pressed. This small bearing, located between the engine crankshaft and the transmission input shaft, allows the input shaft to rotate smoothly when the engine is running but the clutch is disengaged. If the pilot bearing is worn or damaged, it
-
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
1 pointsA manual transmission slips out of third gear. Which of the following MOST Iikely causes this condition?
Correct
A weak detent spring is the most likely cause of a manual transmission slipping out of third gear. The detent spring is a spring-loaded mechanism inside the transmission that helps hold the shift lever securely in gear. When the spring becomes weak or worn, it may fail to maintain proper gear engagement, allowing the transmission to pop out of gear—an issue commonly seen in older manual transmissions.
While worn bushings or a worn shifter bushing can cause a loose or imprecise feel when shifting, they are less likely to cause the transmission to actually slip out of gear. Similarly, high fluid pressure is not a typical cause of this problem; it may contribute to other issues such as harsh or noisy shifting but does not directly affect gear retention.
Incorrect
A weak detent spring is the most likely cause of a manual transmission slipping out of third gear. The detent spring is a spring-loaded mechanism inside the transmission that helps hold the shift lever securely in gear. When the spring becomes weak or worn, it may fail to maintain proper gear engagement, allowing the transmission to pop out of gear—an issue commonly seen in older manual transmissions.
While worn bushings or a worn shifter bushing can cause a loose or imprecise feel when shifting, they are less likely to cause the transmission to actually slip out of gear. Similarly, high fluid pressure is not a typical cause of this problem; it may contribute to other issues such as harsh or noisy shifting but does not directly affect gear retention.
-
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
1 pointsA manual transmission vehicle’s clutch pedal feels hard and binding. The clutch sticks and does not disengage entirely. Which of the following is MOST LIKELY to be the cause of this condition?
Correct
Based on the symptoms described—a hard, binding clutch pedal and the clutch sticking or failing to fully disengage—the most likely cause is a faulty clutch release bearing.
The clutch release bearing disengages the clutch when the pedal is pressed. If it becomes worn or damaged, it can prevent the clutch from releasing completely, making it difficult to shift gears. It can also create resistance in the pedal, causing it to feel stiff or binding.
While issues with the input shaft or input shaft bearing might produce some similar symptoms, they are less common and typically result in different signs, such as grinding or whining noises. The vacuum booster, which assists brake pedal effort, does not play a role in clutch operation and is unlikely to be related to this issue.
Incorrect
Based on the symptoms described—a hard, binding clutch pedal and the clutch sticking or failing to fully disengage—the most likely cause is a faulty clutch release bearing.
The clutch release bearing disengages the clutch when the pedal is pressed. If it becomes worn or damaged, it can prevent the clutch from releasing completely, making it difficult to shift gears. It can also create resistance in the pedal, causing it to feel stiff or binding.
While issues with the input shaft or input shaft bearing might produce some similar symptoms, they are less common and typically result in different signs, such as grinding or whining noises. The vacuum booster, which assists brake pedal effort, does not play a role in clutch operation and is unlikely to be related to this issue.
-
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
1 pointsA problematic axle is being examined in a front-wheel-drive vehicle. Technician A claims that a faulty outboard CV joint generates the most noise when turning. According to Technician B, a malfunctioning inboard CV joint generates the most noise when accelerating and decelerating. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Both technicians are correct. A worn outboard CV joint usually produces the most noise while turning, as it transmits power to the wheels at sharp angles during cornering. In contrast, a faulty inboard CV joint typically makes noise during acceleration or deceleration, since it handles power transfer while the suspension moves in and out under load. Each joint plays a different role depending on driving conditions, which is why their symptoms appear at different times.
Incorrect
Both technicians are correct. A worn outboard CV joint usually produces the most noise while turning, as it transmits power to the wheels at sharp angles during cornering. In contrast, a faulty inboard CV joint typically makes noise during acceleration or deceleration, since it handles power transfer while the suspension moves in and out under load. Each joint plays a different role depending on driving conditions, which is why their symptoms appear at different times.
-
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
1 pointsWhich driveline component is going to ONLY be found on all-wheel-drive vehicles with the function of transferring and controlling torque between the front and rear wheels?
 Correct
Correct
The viscous coupling is exclusive to AWD models. All other components are found on both FWD and AWD configurations.
Incorrect
The viscous coupling is exclusive to AWD models. All other components are found on both FWD and AWD configurations.
-
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
1 pointsWhich of the following is true about the part in this picture? Correct
Correct
The flywheel is bolted to the pressure plate, but it’s important to clarify that the component shown in the image is a clutch disc, not a pressure plate.
When the diaphragm spring fingers are depressed, they release the pressure plate’s clamping force, allowing the clutch disc to rotate freely. The clutch disc contains the friction material and is positioned between the flywheel and the pressure plate. It is splined to the transmission’s input shaft, enabling it to transmit engine power to the drivetrain.
The pressure plate, which is bolted to the flywheel, applies pressure to the clutch disc to engage the drivetrain. While it may help dampen some vibrations, its primary role is to maintain consistent contact between the flywheel and clutch disc, not to reduce engine vibration.
Incorrect
The flywheel is bolted to the pressure plate, but it’s important to clarify that the component shown in the image is a clutch disc, not a pressure plate.
When the diaphragm spring fingers are depressed, they release the pressure plate’s clamping force, allowing the clutch disc to rotate freely. The clutch disc contains the friction material and is positioned between the flywheel and the pressure plate. It is splined to the transmission’s input shaft, enabling it to transmit engine power to the drivetrain.
The pressure plate, which is bolted to the flywheel, applies pressure to the clutch disc to engage the drivetrain. While it may help dampen some vibrations, its primary role is to maintain consistent contact between the flywheel and clutch disc, not to reduce engine vibration.
-
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
1 pointsA vehicle is having a trouble in shifting, particularly into first gear. Technician A says the first speed blocking ring is the MOST likely reason. However, technician B thinks the clutch could be out of adjustment. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Difficulty shifting into first gear is often a sign of a clutch system issue. The clutch’s primary function is to disengage engine power from the transmission, allowing for smooth gear engagement. If the clutch is out of adjustment or not fully disengaging, it can make shifting into first gear—and sometimes other gears—difficult or even impossible.
Technician A’s claim that the first speed blocking ring is the likely cause is not accurate in this scenario. While the blocking ring helps synchronize gear engagement in manual transmissions, it typically affects more than just first gear when faulty. If the problem is isolated to first gear, a clutch disengagement issue is a more probable cause than a worn blocking ring.
Incorrect
Difficulty shifting into first gear is often a sign of a clutch system issue. The clutch’s primary function is to disengage engine power from the transmission, allowing for smooth gear engagement. If the clutch is out of adjustment or not fully disengaging, it can make shifting into first gear—and sometimes other gears—difficult or even impossible.
Technician A’s claim that the first speed blocking ring is the likely cause is not accurate in this scenario. While the blocking ring helps synchronize gear engagement in manual transmissions, it typically affects more than just first gear when faulty. If the problem is isolated to first gear, a clutch disengagement issue is a more probable cause than a worn blocking ring.
-
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
1 pointsThe technicians find that the backing plate and brake shoes are wet with fluid after removing a rear brake drum from a light truck with a solid rear axle. According to Technician A, this contamination could be caused by a leaking wheel cylinder. According to Technician B, the reason could be a leaking axle seal. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Both Technician A and Technician B could be correct, as both a leaking wheel cylinder and a leaking axle seal can lead to fluid contamination on the backing plate and brake shoes.
The wheel cylinder, a key component in drum brake systems, applies hydraulic pressure to the brake shoes. If it leaks, brake fluid can seep out and coat nearby parts, including the backing plate and brake shoes, reducing braking performance.
Similarly, the axle seal—located at the end of the axle shaft—prevents differential fluid from leaking onto the brakes. When it fails, gear oil can escape and contaminate the same components, leading to similar symptoms. Therefore, both sources of leakage should be inspected when fluid contamination is found in the brake assembly
Incorrect
Both Technician A and Technician B could be correct, as both a leaking wheel cylinder and a leaking axle seal can lead to fluid contamination on the backing plate and brake shoes.
The wheel cylinder, a key component in drum brake systems, applies hydraulic pressure to the brake shoes. If it leaks, brake fluid can seep out and coat nearby parts, including the backing plate and brake shoes, reducing braking performance.
Similarly, the axle seal—located at the end of the axle shaft—prevents differential fluid from leaking onto the brakes. When it fails, gear oil can escape and contaminate the same components, leading to similar symptoms. Therefore, both sources of leakage should be inspected when fluid contamination is found in the brake assembly
-
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
1 pointsA constant-mesh manual transmission is difficult to rotate. Technician A believes the needle bearings in the countershaft gear assembly are defective. According to Technician B, this binding could be caused by worn tapered roller bearings. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Defective needle bearings in the countershaft gear assembly can definitely cause binding and make the transmission difficult to rotate. These bearings support the countershaft, which transfers power from the input shaft to the output shaft. When needle bearings become worn or damaged, they can restrict the countershaft’s movement, leading to binding.
Worn tapered roller bearings can also contribute to binding in a manual transmission. These bearings are commonly used to support shafts and gears, and if they wear out, they can lead to misalignment or excessive friction, making it hard to rotate the transmission components smoothly.
Incorrect
Defective needle bearings in the countershaft gear assembly can definitely cause binding and make the transmission difficult to rotate. These bearings support the countershaft, which transfers power from the input shaft to the output shaft. When needle bearings become worn or damaged, they can restrict the countershaft’s movement, leading to binding.
Worn tapered roller bearings can also contribute to binding in a manual transmission. These bearings are commonly used to support shafts and gears, and if they wear out, they can lead to misalignment or excessive friction, making it hard to rotate the transmission components smoothly.
-
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
1 pointsAn older 4WD (four-wheel-drive) truck using Cardan U-joints to drive the front wheels experiences a vibration whenever turning and accelerating rapidly. Technician A believes the rear drive shaft may be out-of-balance. But technician B states this is a normal condition for Cardan U-joints used on early 4WD vehicles. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Vibration is a common issue associated with conventional Cardan U-joints, which are used to drive the front wheels. Technician A is incorrect in stating that a rear driveshaft imbalance causes an out-of-balance driveshaft. In reality, an imbalanced rear driveshaft results in constant vibration, regardless of speed or load, rather than causing the driveshaft itself to become out of balance.
Incorrect
Vibration is a common issue associated with conventional Cardan U-joints, which are used to drive the front wheels. Technician A is incorrect in stating that a rear driveshaft imbalance causes an out-of-balance driveshaft. In reality, an imbalanced rear driveshaft results in constant vibration, regardless of speed or load, rather than causing the driveshaft itself to become out of balance.
-
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
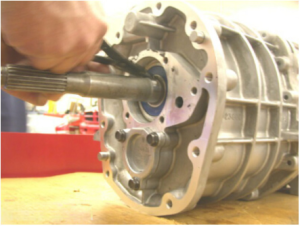
1 pointsWhat operation is being performed in this photo?
 Correct
Correct
It’s important to emphasize that removing the snap ring and input shaft bearing should be performed only by someone with the appropriate tools and experience, as improper handling can lead to damage or injury.
Incorrect
It’s important to emphasize that removing the snap ring and input shaft bearing should be performed only by someone with the appropriate tools and experience, as improper handling can lead to damage or injury.
-
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
1 pointsWhich of the below options is NOT a symptom of a failing constant velocity (CV) joint?
Correct
Common signs of a failing CV joint include a clunking noise during acceleration from a stop, popping or clicking sounds when turning, and vibrations at specific speeds. These symptoms typically point to worn or damaged CV joints that may require replacement. However, a whining noise while slowing down is more often related to problems with the brakes or wheel bearings, rather than the CV joint.
Incorrect
Common signs of a failing CV joint include a clunking noise during acceleration from a stop, popping or clicking sounds when turning, and vibrations at specific speeds. These symptoms typically point to worn or damaged CV joints that may require replacement. However, a whining noise while slowing down is more often related to problems with the brakes or wheel bearings, rather than the CV joint.
-
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
1 pointsIn a vehicle with a no-start condition, a technician is checking a clutch safety switch. Which of the following is NOT correct about this switch?
Correct
The statement “The meter should display continuity 0.00 with the pedal out and the switch contacts open” is incorrect regarding the clutch safety switch. When the clutch pedal is out (not depressed), the switch contacts should be closed, allowing continuity through the circuit. When the pedal is depressed, the contacts should open, breaking the circuit. Therefore, the meter should show continuity when the pedal is out, and no continuity when the pedal is pressed.
The other statements are accurate. The clutch safety switch is part of the starting system and prevents the engine from starting unless the clutch pedal is depressed. A multimeter is a suitable tool for diagnosing and testing the clutch safety switch circuit.
Incorrect
The statement “The meter should display continuity 0.00 with the pedal out and the switch contacts open” is incorrect regarding the clutch safety switch. When the clutch pedal is out (not depressed), the switch contacts should be closed, allowing continuity through the circuit. When the pedal is depressed, the contacts should open, breaking the circuit. Therefore, the meter should show continuity when the pedal is out, and no continuity when the pedal is pressed.
The other statements are accurate. The clutch safety switch is part of the starting system and prevents the engine from starting unless the clutch pedal is depressed. A multimeter is a suitable tool for diagnosing and testing the clutch safety switch circuit.
-
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
1 pointsTechnician A recommends checking the clearance between the shift fork and the synchronizer sleeve with a feeler gauge. According to Technician B, a bent shift rail will cause hard shifting. Who is CORRECT?
Correct
Technician A’s recommendation to measure the clearance between the shift fork and the synchronizer sleeve using a feeler gauge is a sound diagnostic step. The synchronizer assembly ensures that the gear and input shaft are rotating at compatible speeds before engagement, reducing wear and preventing gear grinding. Incorrect clearance between the shift fork and synchronizer sleeve can lead to hard shifting or grinding during gear changes.
Technician B is also correct in suggesting that a bent shift rail could contribute to hard shifting. The shift rail guides the movement of the shift forks to engage specific gears. If it’s bent or damaged, it can hinder smooth fork movement, resulting in shifting difficulties or gear engagement issues.
Incorrect
Technician A’s recommendation to measure the clearance between the shift fork and the synchronizer sleeve using a feeler gauge is a sound diagnostic step. The synchronizer assembly ensures that the gear and input shaft are rotating at compatible speeds before engagement, reducing wear and preventing gear grinding. Incorrect clearance between the shift fork and synchronizer sleeve can lead to hard shifting or grinding during gear changes.
Technician B is also correct in suggesting that a bent shift rail could contribute to hard shifting. The shift rail guides the movement of the shift forks to engage specific gears. If it’s bent or damaged, it can hinder smooth fork movement, resulting in shifting difficulties or gear engagement issues.
-
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
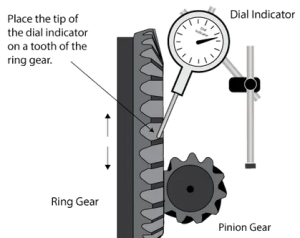
1 pointsThe measurement taken in the given image is checking for
_________. Correct
Correct
Measuring backlash in a rear axle is a critical step in diagnosing and troubleshooting potential problems with the differential and gearset. Backlash refers to the small gap or clearance between the meshing teeth of the ring gear and pinion gear. This spacing allows for proper gear engagement and smooth operation within the differential.
Incorrect
Measuring backlash in a rear axle is a critical step in diagnosing and troubleshooting potential problems with the differential and gearset. Backlash refers to the small gap or clearance between the meshing teeth of the ring gear and pinion gear. This spacing allows for proper gear engagement and smooth operation within the differential.
